What is a Tympanogram? Understanding Tympanometry and the Different Tympanogram Types
If you’ve been experiencing ear discomfort, hearing difficulties, or recurrent ear infections, a tympanogram can offer valuable insights into your middle ear health and function. A tympanogram is an essential diagnostic test that helps detect problems in the middle ear by measuring how your eardrum responds to changes in air pressure. This simple, painless test is critical in diagnosing conditions early, allowing for timely treatment and better hearing outcomes.
In this article, we will explore what a tympanogram is, why tympanometry matters for ear health, and explain the various tympanogram types in detail — including the often discussed type C tympanogram. We will also discuss when you should get tested and how The Hearing Centre in Singapore can support your hearing health journey.
What is a Tympanogram?
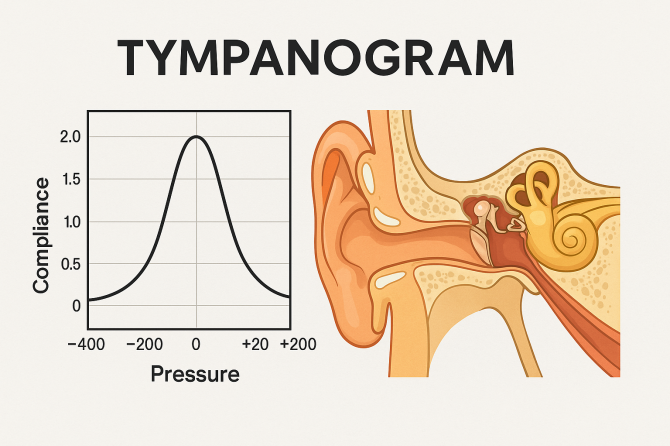
A tympanogram is the visual graph or chart produced during a tympanometry test, which evaluates the condition of the middle ear by measuring the mobility of the eardrum (also called the tympanic membrane). Tympanometry is a diagnostic procedure performed by audiologists or ear specialists that provides objective information about how well the middle ear system is functioning.
During the test, a small device known as a tympanometer is gently placed in your ear canal. This device changes the air pressure inside your ear canal and emits a soft probe tone. By varying the pressure and recording the sound that bounces back from your eardrum, the tympanometer plots a graph — the tympanogram — which reflects the flexibility or stiffness of your eardrum and the pressure within your middle ear.
This data helps professionals detect middle ear abnormalities that might not be apparent through hearing tests alone, making the tympanogram a vital part of a comprehensive hearing evaluation.
Why Tympanometry Matters
Tympanometry provides crucial information that can’t be obtained from hearing tests alone. The importance of tympanometry includes:
- Diagnosing Middle Ear Conditions: Tympanometry can detect fluid buildup (such as in otitis media), eardrum perforations, or Eustachian tube dysfunction, conditions which can affect hearing and cause discomfort.
- Guiding Treatment: Early diagnosis of middle ear problems can prevent complications such as chronic infections or hearing loss.
- Relevance for All Ages: From infants and toddlers to seniors, tympanometry is essential for assessing ear health across the lifespan. It is especially valuable in children where early detection can improve speech and language development outcomes.
- Pre-Hearing Aid Evaluation: Before fitting hearing aids, tympanometry confirms that the middle ear is healthy enough to support device use, avoiding fitting on potentially compromised ears.
In summary, tympanometry is a non-invasive, reliable, and quick method to ensure your middle ear is functioning properly.
Understanding Tympanogram Types
There are several tympanogram types categorized mainly by Jerger’s classification system, which helps clinicians understand middle ear status based on the shape and peak of the tympanogram graph. Each type indicates different conditions or health levels of the ear.
The main tympanogram types include:
- Type A Tympanogram: This type shows a normal peak near zero pressure, indicating normal middle ear function and healthy eardrum mobility.
- Type As Tympanogram: The peak is shallow, meaning reduced eardrum movement. This can suggest stiffening of the middle ear bones, as seen in conditions like otosclerosis.
- Type Ad Tympanogram: Shows an abnormally high peak, reflecting excessive mobility of the eardrum, which may occur due to ossicular discontinuity or a flaccid eardrum.
- Type B Tympanogram: Characterized by a flat line with no clear peak, indicating very little or no eardrum movement. This is commonly caused by fluid in the middle ear or a perforated eardrum.
- Type C Tympanogram: This type presents a peak shifted toward negative pressure values, showing negative middle ear pressure. It typically suggests early Eustachian tube dysfunction or the onset of middle ear infection.
Understanding these tympanogram types helps clinicians interpret test results correctly and tailor treatment plans effectively.
More about Type C Tympanogram
The type C tympanogram is particularly important because it indicates negative pressure in the middle ear cavity, often caused by Eustachian tube dysfunction. The Eustachian tube normally equalizes air pressure between the middle ear and the environment, but when it is blocked or not working properly, pressure drops below normal. This negative pressure can lead to discomfort, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and potential progression toward infection if untreated.
Recognizing a type C tympanogram early enables healthcare professionals to recommend appropriate management strategies, such as decongestants, nasal sprays, or monitoring to prevent worsening of symptoms.
What Does Each Tympanogram Type Tell You?
Interpreting the different tympanogram types allows audiologists and ENT specialists to:
- Type A: Confirm healthy ear function. No treatment needed unless hearing loss is present.
- Type As: Detect stiffening or limited eardrum movement. May need further investigation or monitoring for conditions like otosclerosis.
- Type Ad: Suggest hypermobility or damage to the ossicles or eardrum. Referral for further medical evaluation is advised.
- Type B: Indicate fluid presence or perforation in the middle ear. Immediate treatment or specialist referral is necessary.
- Type C: Highlight early Eustachian tube problems. Early intervention can prevent infection and further complications.
Additionally, these interpretations help decide when to refer a patient for medical treatment or consider hearing aid readiness and customization.
When Should You Get a Tympanometry Test?
Consider booking a tympanometry test if you experience:
- A persistent feeling of ear fullness or pressure
- Difficulty hearing or muffled sounds
- Frequent or recurring ear infections
- Pain or discomfort in the ear
- Delays in speech development (especially in children)
- Symptoms of dizziness or imbalance linked to ear problems
Children, seniors, and individuals exposed to frequent loud noise or ear infections particularly benefit from routine tympanometry screening to detect issues before they become serious.
Tympanometry and Hearing Aids
Tympanometry plays a key role in hearing aid assessment and management by:
- Ensuring there are no middle ear issues such as infections or fluid before device fitting.
- Helping audiologists customize hearing aid settings based on middle ear status.
- Providing a baseline to monitor ear health during hearing aid use.
- Avoiding complications like device discomfort or reduced effectiveness caused by undiagnosed middle ear conditions.
Thus, tympanogram results directly influence the success and comfort of hearing aid users.
How The Hearing Centre Can Help
At The Hearing Centre, our experienced audiologists provide:
- Comprehensive hearing assessments, including advanced tympanometry testing.
- Expert interpretation of tympanogram types, including type C tympanogram findings.
- Real-ear measurements to fine-tune hearing aid fittings for maximum benefit.
- Personalized treatment plans and ongoing follow-up care.
- Trusted service across 5 convenient Singapore locations with over 20 years of expertise.
Our goal is to help you achieve the best possible hearing health with professional care tailored to your unique needs.
Rediscover the joy of hearing with The Hearing Centre! Book your professional tympanometry test today at one of our convenient locations or try our free 5-minute online hearing test. Contact us now for expert care and customized hearing solutions designed just for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What exactly is a tympanogram?
A tympanogram is a graph produced during tympanometry testing that shows how your eardrum moves in response to pressure changes in the ear canal, helping to assess middle ear health.
Q2. How is the tympanometry test performed?
A small probe is placed in the ear canal, which changes the air pressure and plays a soft tone. The device measures the eardrum’s movement and displays it as a tympanogram.
Q3. What do the different tympanogram types indicate?
They indicate various middle ear conditions: Type A is normal, Type As suggests stiffness, Type Ad shows hypermobility, Type B points to fluid or perforation, and Type C reflects negative pressure.
Q4. What does a type C tympanogram mean?
It means there is negative pressure in the middle ear, often caused by Eustachian tube dysfunction or early infection, and usually requires medical attention.
Q5. Is tympanometry painful or uncomfortable?
No, it is a painless, quick, and non-invasive procedure suitable for all ages.
Q6. Can tympanometry detect hearing loss?
Tympanometry evaluates middle ear function but does not measure hearing ability directly. It is used alongside hearing tests for a complete diagnosis.
Q7. Who should get a tympanometry test?
Anyone with ear symptoms, children with speech delays, people with frequent ear infections, and those considering hearing aids should get tested.
Q8. How often should I have tympanometry done?
It depends on your symptoms and risk factors. Audiologists recommend testing when symptoms arise or during regular hearing assessments.
Leave a reply
Leave a reply